Page 126 - FoodFocusThailand No.207 JUNE 2023
P. 126
SCOOP
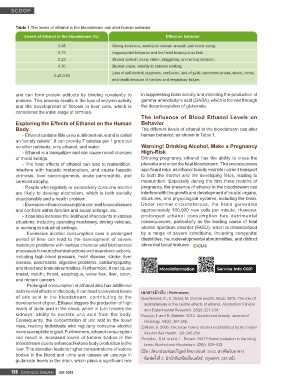
Table 1 The levels of ethanol in the bloodstream can alter human behavior
Levels of ethanol in the bloodstream (%) Effect on behavior
0.08 Wrong decisions, inability to restrain oneself, and mood swing.
0.15 Inappropriate behavior and the heart beating is so fast.
0.23 Slurred speech, blurry vision, staggering, and wrong decision.
0.30 Blurred vision, inability to balance walking.
Loss of self-control, dizziness, confusion, lack of guilt, unconsciousness, shock, coma,
0.45-0.50
and death because of cardiac and respiratory failure.
and can form protein adducts by binding covalently to in suppressing brain activity and inhibiting the production of
proteins. This process results in the loss of enzyme activity gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA), which is formed through
and the development of fibrosis in liver cells, which is the decarboxylation of glutamate.
considered the initial stage of cirrhosis.
The Influence of Blood Ethanol Levels on
Exploring the Effects of Ethanol on the Human Behavior
Body The different levels of ethanol in the bloodstream can alter
- Ethanol contains little or no nutritional value and is called human behavior, as shown in Table 1.
an “empty calorie”. It can provide 7 calories per 1 gram but
no other nutrients, only ethanol, and water. Warning! Drinking Alcohol, Make a Pregnancy
- Ethanol is a tranquilizer and can cause mood changes High-Risk
or mood swings. Drinking pregnancy, ethanol has the ability to cross the
- The toxic effects of ethanol can lead to malnutrition, placenta and enter the fetal bloodstream. This process poses
interfere with hepatic metabolism, and cause hepatic significant risks, as ethanol toxicity restricts nutrient transport
cirrhosis, liver carcinogenesis, acute pancreatitis, and to both the mother and the developing fetus, leading to
cerebral atrophy. malnutrition. Especially during the first three months of
- People who regularly or excessively consume alcohol pregnancy, the presence of ethanol in the bloodstream can
are likely to develop alcoholism, which is both socially interfere with the growth and development of crucial organs,
objectionable and a health problem. structures, and physiological systems, including the brain.
- Excessive ethanol consumption can lead to social issues Under normal circumstances, the brain generates
and conflicts within families and social settings, etc. approximately 100,000 new cells per minute. However,
- It can also increase the likelihood of accidents in various prolonged ethanol consumption has detrimental
situations, including operating machinery, driving vehicles, consequences, particularly as the leading cause of fetal
or working in industrial settings. alcohol spectrum disorder (FASD), which is characterized
Excessive alcohol consumption over a prolonged by a range of severe conditions, including congenital
period of time can lead to the development of severe disabilities, neurodevelopmental abnormalities, and distinct
metabolic problems with various chemical and biochemical abnormal facial features.
processes in neurochemical actions and neurotoxic actions,
including high blood pressure, heart disease, stroke, liver
disease, pancreatitis, digestive problems, cardiomyopathy,
and blood and brain abnormalities. Furthermore, it can cause More Information Service Info C021
breast, mouth, throat, esophagus, voice box, liver, colon,
and rectum cancers.
Prolonged consumption of ethanol also has additional
detrimental effects on the body. It can lead to elevated levels เอกสารอ้างอิง / References
of uric acid in the bloodstream, contributing to the Quertemont, E., K. Grant, M. Correa and M. Arizzi. 2005. The role of
development of gout. Ethanol triggers the production of high acetaldehyde in the central effects of ethanol. Alcoholism Clinical
levels of lactic acid in the blood, which in turn hinders the and Experimental Research. 29(2): 221-234.
kidneys’ ability to excrete uric acid from the body. Ruusyn, I. and R. Bataller. 2013. Alcohol and toxicity. Journal of
Consequently, the concentration of uric acid in the blood Histology. 59(2): 387-388.
rises, making individuals who regularly consume alcohol Zakhari, S. 2006. Overview: how is alcohol metabolized by the body?
more susceptible to gout. Furthermore, ethanol consumption Alcohol Res Health. 29: 245-254.
can result in increased levels of ketone bodies in the Zimatkin, S.M. and A. L. Buben. 2007 Ethanol oxidation in the living
bloodstream due to enhanced ketone body production in the brain. Alcohol and Alcoholism. 42(6): 529–532.
liver. This elevation leads to higher concentrations of ketone นิิธิิยา รััตนิาปนินิท์์และวิิบููลย์ รััตนิาปนินิท์์. 2553. สารัพิิษในิอาหารั.
bodies in the blood and urine and causes an upsurge in
glutamate levels in the brain, which plays a significant role พิิมพิ์ครัั�งท์่� 2. สำานิักพิิมพิ์โอเดี่ยนิสโตรั์, กรัุงเท์พิฯ, 330 หนิ้า.
126 FOOD FOCUS THAILAND JUN 2023
22/5/2566 BE 18:45
122-126_Scoop_������_������.indd 126 22/5/2566 BE 18:45
122-126_Scoop_������_������.indd 126