Page 66 - FoodFocusThailand No.221 August 2024
P. 66
STRONG QC & QA
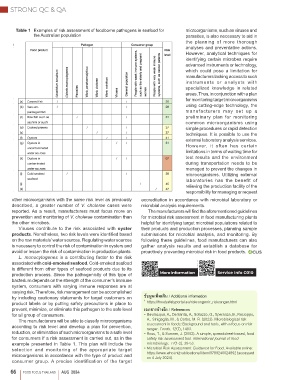
Table 1 Examples of risk assessment of foodborne pathogens in seafood for microorganisms, such as viruses and
the Australian population parasites, is also necessary to aid in
the planning of more thorough
analyses and preventative actions.
However, analytical techniques for
identifying certain microbes require
advanced instruments or technology,
which could pose a limitation for
manufacturers lacking access to such
instruments or analysts with
specialized knowledge in related
areas. Thus, in conjunction with a plan
for monitoring target microorganisms
using cutting-edge technology, the
manufacturers may set up a
preliminary plan for monitoring
common microorganisms using
simple procedures or rapid detection
techniques. It is possible to use the
external laboratory analysis services.
However, it often has certain
limitations in terms of waiting time for
test results and the environment
during transportation needs to be
managed to prevent the changes in
microorganisms. Utilizing external
laboratories has the benefit of
relieving the production facility of the
responsibility for managing or request
other microorganisms with the same risk level as previously accreditation in accordance with microbial laboratory or
described, a greater number of V. cholerae cases were microbial analysis requirements.
reported. As a result, manufacturers must focus more on The manufacturers will find the aforementioned guidelines
prevention and monitoring of V. cholerae contamination than for microbial risk assessment in food manufacturing plants
the other microbes. helpful for identifying target microbial populations related to
Viruses contribute to the risk associated with oyster their products and production processes, planning sample
products. Nonetheless, two risk levels were identified based submissions for microbial analysis, and monitoring. By
on the raw materials’ water sources. Regulating water sources following these guidelines, food manufacturers can also
is necessary to control the risk of contamination in oysters and gather analysis results and establish a database for
avoid or lessen the risk of contamination in production plants. proactively preventing microbial risk in food products.
L. monocytogenes is a contributing factor to the risk
associated with cold-smoked seafood. Cold-smoked seafood
is different from other types of seafood products due to its
production process. Since the pathogenicity of this type of More Information Service Info C010
bacterium depends on the strength of the consumer’s immune
system, consumers with varying immune responses are at
varying risk. Therefore, risk management can be accomplished
by including cautionary statements for target customers on ข้้อมููลเพิ่่�มูเติ่มู / Additional information
1
product labels or by putting safety precautions in place to https://foodsafetyportal.eu/riskranger/rr_riskranger.html
prevent, minimize, or eliminate this pathogen to the safe level เอกสารอ้างอ่ง / References
for all group of consumers. • Bevilacqua, A., De Santis, A., Sollazzo, G., Speranza, B., Racioppo,
The manufacturers will be able to classify microorganisms A., Sinigaglia, M., & Corbo, M. R. (2023). Microbiological risk
according to risk level and develop a plan for prevention, assessment in foods: Background and tools, with a focus on risk
ranger. Foods, 12(7), 1483.
reduction, or elimination of such microorganisms to a safe level • Ross, T., & Sumner, J. (2002). A simple, spreadsheet-based, food
for consumers if a risk assessment is carried out, as in the safety risk assessment tool. International journal of food
example presented in Table 1. This plan will include the microbiology, 77(1-2), 39-53.
selection and monitoring of the appropriate target • Microbial Risk Assessment: Guidance for Food. Available online:
https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/9789240024892 (accessed
microorganisms in accordance with the type of product and on 4 July 2024).
consumer group. A precise identification of the target
66 FOOD FOCUS THAILAND AUG 2024
24/7/2567 BE 13:07
61-66_Strong QC&QA_������.indd 66 24/7/2567 BE 13:07
61-66_Strong QC&QA_������.indd 66