SAFETY
ALERT
69
AUG 2017 FOOD FOCUSTHAILAND
MicrobialControl
i
nPoultryProcessingusing
PAA InterventionStrategy
Disinfection is part of the basic program that reduces the
risk from inline contamination during poultry processing. It
helps inkeeping the foodsafe forconsumers,extendproduct
shelf-life&complywithglobal foodsafety regulations.Such
as
Salmonella,Campylobacter
and
E.coli
occur in livepoultry
andgets transferredduring processing.
Disinfectionprocesscanbedonebyusingsteam, heat or usesome
disinfectantssuchaschlorine, iodine, quartzcompoundsandPeracetic
acid, etc. Since each disinfectant has different advantages and
disadvantages.
Choosing the right disinfectant is the key challengeencounteredby
various processors in modern era. The key criteria for selection are
efficacyagainst
Salmonella
and
E. coli
,Yield/productivity, the impact on
the health of consumers, environmental impact of using a particular
chemistryasdisinfectantandconforming toglobal foodsafety regulation.
Perennially chlorine was the key chemical used as a primary
disinfectantacross food industries;however, ithasadverseenvironmental
impact and some studiesmentioned its carcinogenic effects on human
life. Hence scientist has been studying the environmentally safe PAA
chemistry against chlorine for decades.
“Peracetic Acid (PAA)” has been recognized as a key intervention
chemical for poultrydisinfection inUSmarket (USFDA /EPA) andsome
European countries (DEFRA of England) and it’s widely used by
processors.RecentlyJapanhasapprovedusageofPAA inpoultry,meat
and fruit&vegetableasshelf lifeextenderandmicrobial control reagent.
Various studies have been done globally to validate the efficacy of
PAAagainst chlorine, oneof the study inUSA is as below
PAAhasabout30%higherefficacyagainstChlorineandgivesbetter
sensory / texture after treatment.
InUSApercentage rejection due to
Salmonella
has gone less than
3-4%with intervention of PAAwhichwas originally about 20% in 2005.
Currently in Thailand we observe about 20-25% of chicken carcasses
shows
Salmonella
positiveevenChlorine isused in theWater supplyof
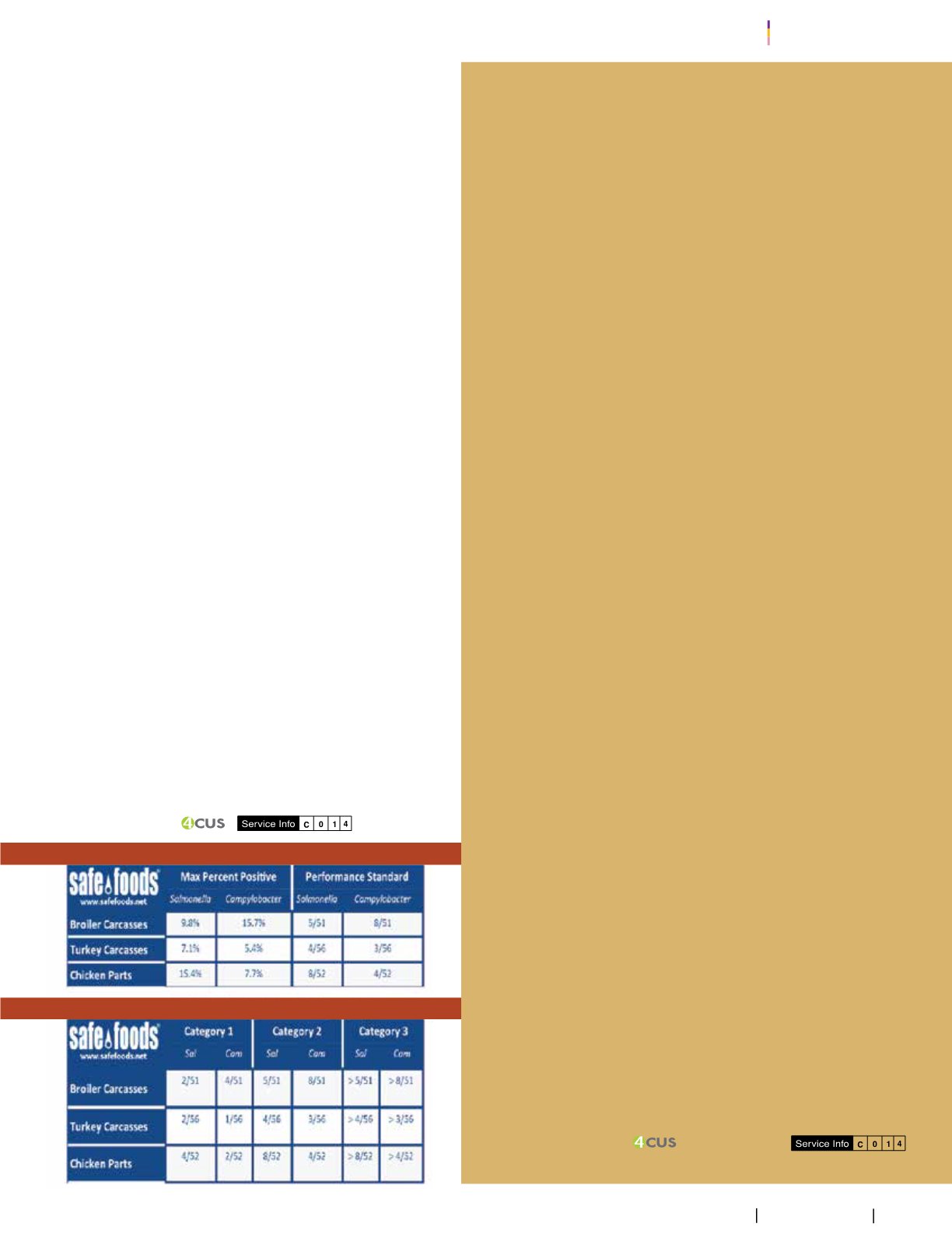
the plant. USDA-FSIS performance standard for poultry for Salmonella
level (2015) less than 9.8% or 5/51.
Key InterventionPoints for PAA;
• Approved for spray, rinse, dip and chiller application for poultry
• Approved up tomax 220ppm (21CFR 173.370, USFDA)
• EPAapproved as pesticide (EPA# 65402-1, EPA# 65402-3)
As the global food and environment safety regulationswill become
morestringentwe foreseePAAchemistry replacing the traditionalchlorine
chemistry for key food.
ทดลองดั
งกล่
าวของประเทศสหรั
ฐอเมริ
กาได้
แสดงให้
เห็
นถึ
งการลดลงของ
เชื้
อ
Salmonella
ในกระบวนการแช่
เย็
นอาหารจากการทดลองใช้
กรดเปอร์
-
อะซิ
ติ
กความเข้
มข้
น85ppm เที
ยบกั
บการใช้
คลอรี
นความเข้
มข้
น30ppm
พบว่
ามี
การลดลงของเชื้
อ
Salmonella
ร้
อยละ91.8และ66.0ตามล�
ำดั
บ
จากผลการศึ
กษาพบว่
ากรดเปอร์
อะซิ
ติ
กมี
ประสิ
ทธิ
ภาพในการฆ่
าเชื้
อ
จุ
ลิ
นทรี
ย์
มากกว่
าคลอรี
นถึ
งร้
อยละ 30 และยั
งให้
ผลิ
ตภั
ณฑ์
ที่
มี
ลั
กษณะ
ทางประสาทสั
มผั
ส รวมถึ
งรั
กษาคุ
ณภาพของสิ
นค้
าได้
ดี
กว่
าอี
กด้
วย
มี
การรายงานของสหรั
ฐอเมริ
กาเมื่
อปี
2548พบว่
ามี
การปฏิ
เสธสิ
นค้
า
อั
นเนื่
องมาจากการปนเปื้
อนเชื้
อ
Salmonella
ลดลงเหลื
อเพี
ยงร้
อยละ3-4
เท่
านั้
นหลั
งจากมี
การน�
ำสารฆ่
าเชื้
อกรดเปอร์
อะซิ
ติ
กมาใช้
ซึ่
งแต่
เดิ
มมี
การ
ปฏิ
เสธสิ
นค้
ามากถึ
งร้
อยละ20อั
นเนื่
องมาจากการตรวจพบการปนเปื้
อน
ของเชื้
อดั
งกล่
าวในสิ
นค้
าไก่
แปรรู
ป ส�
ำหรั
บประเทศไทยก็
มี
การรายงาน
พบซากสั
ตว์
ปี
กที่
มี
การปนเปื้
อนของเชื้
อ
Salmonella
อยู่
ประมาณร้
อยละ
20-25แม้
ว่
าจะมี
การใช้
คลอรี
นในระบบน�้
ำล้
างของโรงงานแล้
วก็
ตาม
ทั้
งนี้
หลั
กเกณฑ์
แนวทางปฏิ
บั
ติ
ตามมาตรฐาน FSIS ส�
ำหรั
บ
สถานประกอบการเพื่
อลดปริ
มาณจุ
ลิ
นทรี
ย์
ก่
อโรค เช่
น
Salmonella
ได้
ก�
ำหนดไว้
ว่
าปริ
มาณเชื้
อจุ
ลิ
นทรี
ย์
ที่
ตรวจพบต้
องน้
อยกว่
าร้
อยละ 9.8
หรื
อที่
ระดั
บ5/51
การใช้
กรดเปอร์
อะซิ
ติ
กในการฆ่
าเชื้
อจุ
ลิ
นทรี
ย์
ก่
อโรค:
• กรดเปอร์
อะซิ
ติ
กได้
รั
บการยอมรั
บให้
ใช้
ในอุ
ตสาหกรรมสั
ตว์
ปี
ก
ทั
้
งรู
ปแบบการสเปรย์
หรื
อฉี
ด พ่
น การล้
าง และการจุ
่
มลงในสารฆ่
าเชื้
อ
เป็
นต้
น
• ความเข้
มข้
นสู
งสุ
ดของกรดเปอร์
อะซิ
ติ
กที่
ใช้
ได้
คื
อ 220 ppm
(21CFR173.370, USFDA)
• กรดเปอร์
อะซิ
ติ
กได้
รั
บอนุ
ญาตให้
ใช้
เป็
นสารเคมี
ในการฆ่
าเชื
้
อได้
ตามมาตรฐานEPA (EPA#65402-1, EPA#65402-3)
อย่
างไรก็
ตาม ปั
จจุ
บั
นนี้
กฎระเบี
ยบด้
านความปลอดภั
ยอาหารและ
สิ่
งแวดล้
อมทั่
วโลกมี
ความเข้
มงวดมากขึ้
น ดั
งนั้
น จึ
งเป็
นที่
คาดหวั
งว่
า
การใช้
กรดเปอร์
อะซิ
ติ
กในการฆ่
าเชื้
อจุ
ลิ
นทรี
ย์
ก่
อโรคจะสามารถเข้
ามา
แทนที่
การใช้
คลอรี
นแบบดั้
งเดิ
มในอุ
ตสาหกรรมอาหารต่
อไปได้
ที่
มา:www.safefoods.net/blog/2016/feb/26/three-implications-of-usda-performance-
standards/
USDA-FSISEstablishment CategoryRequirements
USDA-FSISPerformanceStandards forPoultryProcessing


