Food FocusThailand
AUGUST 2015
35
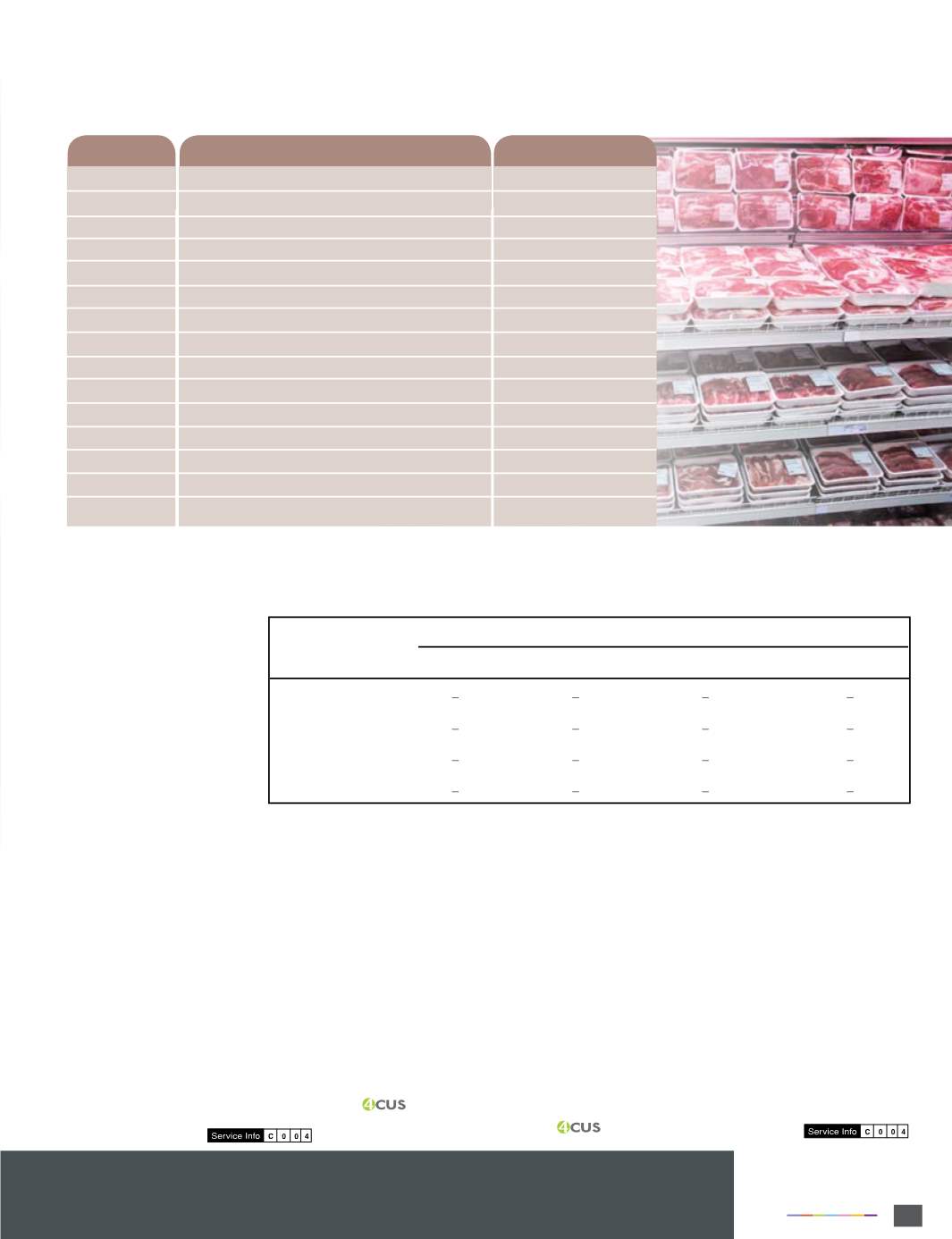
ตารางที่
1
ตั
วอย่
างการเรี
ยกคื
นสิ
นค้
าเมื่
อมี
การตรวจพบการปนเปื้
อนเชื้
อจุ
ลิ
นทรี
ย์
ในผลิ
ตภั
ณฑ์
อาหาร
Table1
Examples of foodproduct recallswhenmicrobial contamination is found
เพื่
อป้
องกั
นไม่
ให้
เกิ
ดการปนเปื
้
อน
ในผลิ
ตภั
ณฑ์
โดยใช้
วิ
ธี
การสวอป
พื้
นผิ
วอุ
ปกรณ์
และสิ่
งแวดล้
อมใน
กระบวนการผลิ
ต
การสวอปให้
มี
ประสิ
ทธิ
ภาพ
สู
งสุ
ดนั้
น มี
ปั
จจั
ยส�
ำคั
ญที่
ต้
องค�
ำนึ
ง
อยู
่
3 ประการ ได้
แก่
จุ
ดทดสอบ
พื้
นผิ
วบริ
เวณ ณ จุ
ดทดสอบ และ
ที
่
ส�
ำคั
ญคื
อเรื่
องของคุ
ณสมบั
ติ
ของ
อุ
ปกรณ์
ที่
ใช้
ในการสวอป ซึ่
งจะ
ต้
องมี
ความสามารถในการเก็
บและ
ปลดปล่
อยเชื้
อจุ
ลิ
นทรี
ย์
ได้
อย่
างมี
Products
Date
Microorganism
Steak andGroundBeef
“TurkeySprinkles” DogFood
KievStuffedChicken
CaribbeanFruit &Nut MixWithMacadamiaNuts
Trail Mix, BulkMacadamiaNuts
NatureRawCashews
RawMacadamiaNuts
Soybean andMungBeanSprouts
BottledWater
Ready-to-eat pork and beef
Raw goat milk feta cheese
DogTreats
CanadianMushrooms
RawMacadamiaNuts
SmokedAndouilleSausage
July 3, 2015
July 3, 2015
July 2, 2015
July 1, 2015
June29, 2015
June27, 2015
June26, 2015
June23, 2015
June22, 2015
June20, 2015
June20, 2015
June19, 2015
June19, 2015
June13, 2015
June12, 2015
E. coli
O157:H7
Salmonella
Salmonella
Enteritidis
Salmonella
Salmonella
Salmonella
Salmonella
Listeriamonocytogenes
E. coli
Listeriamonocytogenes
Listeria
Salmonella
Listeria
Salmonella
Listeriamonocytogenes
ที่
มา/Source:
FoodSafetyNews (
For themost effectiveswab testing, thereare three important factors
to consider, namely: thepoint of testing; the surfaceareaat thepoint of
testing; andmost importantly the properties of the device used for the
swab test—it must be able to both collect and releasemicroorganisms
effectively.
Table2shows that swabdevicesmadeof foam rubber, sponge, and
gauze effectively collect and release bacteria better than swab devices
made from cotton.
From Table 1, “Examples of food product recalls when microbial
contamination is found,” it is evident that themajority of contamination
is from pathogenic microorganisms. Therefore, we must monitor for
pathogens in theproductionenvironment. It is said, that if anorganism
is found in the environment, there is a 70% chance of it getting into
the food (IAFP ROME 2007).Current pathogen testing technology is
developingsignificantly,and includes finding theDNAofpathogenswhich
mustbemonitoredbyusing IsothermalDNAAmplificationcombinedwith
BioluminescenceDetection.Such technologycanprovide fast,accurate,
and reliable test results, which allow for quick and efficient handling of
problems.
ตารางที่
2
ปริ
มาณร้
อยละโดยเฉลี่
ยของเชื้
อแบคที
เรี
ยที่
ปลดปล่
อยและเก็
บโดยอุ
ปกรณ์
สวอปแบบต่
างๆหลั
งจากการเพาะเชื้
อ
Table2
Themeanpercentage of bacterial releasedand recovery from different types of swabs after direct inoculation
ประสิ
ทธิ
ภาพ
จากตารางที่
2 พบว่
าอุ
ปกรณ์
สวอปที
ท�
ำจากโฟม แผ่
นฟองน�้
ำ และผ้
ากอซ
มี
ประสิ
ทธิ
ภาพในการเก็
บและปลดปล่
อยเชื้
อจุ
ลิ
นทรี
ย์
ได้
ดี
กว่
าอุ
ปกรณ์
สวอปที่
ท�
ำ
จากส�
ำลี
จากตารางที่
1ตั
วอย่
างการเรี
ยกคื
นสิ
นค้
าจะเห็
นว่
าส่
วนใหญ่
เป็
นการปนเปื
้
อน
ของเชื้
อจุ
ลิ
นทรี
ย์
ก่
อโรค เราจึ
งต้
องเฝ้
าระวั
งเชื้
อก่
อโรคในสิ่
งแวดล้
อมการผลิ
ตด้
วย
ดั
งมี
ค�
ำกล่
าวที่
ว่
าหากพบการปนเปื้
อนเชื้
อเพี
ยงหนึ่
งตั
วในสิ่
งแวดล้
อมมี
โอกาสถึ
ง
ร้
อยละ 70 ที่
จะเกิ
ดการปนเปื
้
อนในอาหารได้
(IAFP Rome 2007) โดยปั
จจุ
บั
น
เทคโนโลยี
การทดสอบเชื้
อก่
อโรคมี
การพั
ฒนามากขึ้
น เช่
น การหา DNA ของ
เชื้
อก่
อโรคที่
ต้
องการตรวจสอบโดยใช้
อุ
ณหภู
มิ
เดี
ยว (Isothermal DNA
amplification)ผสานกั
บวิ
ธี
การตรวจวั
ดการเรื
องแสงที่
เกิ
ดขึ้
น (Bioluminescence
detection)ให้
ผลการทดสอบที่
รวดเร็
วถู
กต้
องแม่
นย�
ำและมี
ความน่
าเชื่
อถื
อท�
ำให้
สามารถจั
ดการปั
ญหาได้
อย่
างทั
นท่
วงที
และมี
ประสิ
ทธิ
ภาพ
เอกสารอ้
างอิ
ง/References
- FoodSafetyNews :
/
- Effect of swabbing techniqueonamount of bacteria from foodcontact surfaces. Department of FoodTechnology, Faculty of Science,
ChulalongkornUniversity,Department of FoodScienceandTechnology, FacultyofMarineScience, TokyoUniversityofMarineScience
andTechnology.
Swab type
Bacterial
cotton
PU foam
gauze
sponge
E. coli
S. aureus
S.
Typhimurium
L. monocytogenes
87.17 + 1.41
e
84.43 + 1.13
f
80.76 + 2.42
g
81.62 + 0.26
g
99.34 + 0.66
a
96.72 + 1.78
b,c
95.71 + 1.50
c,d
97.76 + 1.43
a,b,c
97.82 + 0.70
a,b
97.55 + 1.00
a,b,c
93.85 + 0.70
d
97.94 + 0.63
a,b
98.98 + 0.61
a
99.07 + 0.41
a
94.09 + 0.80
d
98.49 + 0.38
a,b


